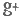Hot Forging And Casting
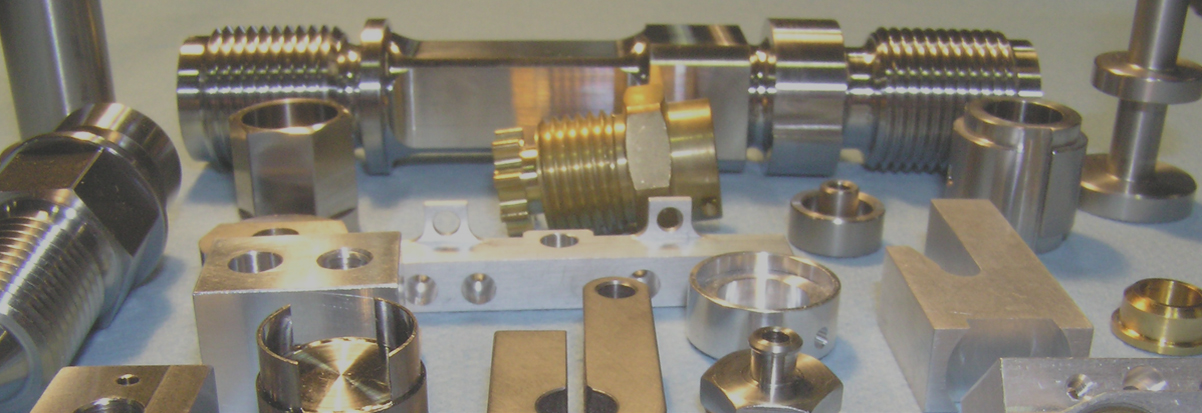
Forged brass welding torch components
Product Details
Forging is a manufacturing process during which presses, hammers, and dies are used to force metals into various shapes. Forging can be done at room temperature (cold forging) or metal temperatures of over 1000 degrees Celsius (hot forging). The forged parts can weigh from a few ounces to hundreds of tons.
The Art of Forging
While the earliest signs of metalworking date back to Mesopotamia around 4500 B.C., the art of forging flourished between the 10th and 12th centuries A.D. It was during this period that the Romans discovered that water, and the power that it was capable of generating, could be used to operate bellows and hammers.
The steam engine of the 19th century ushered in the era of modern forging. Electrical power and the development of explosive forming soon followed. At its earliest stages, forging produced decorative objects from precious metals. Today, it’s a global process with many applications in every industry.
Why Use Forgings?
Forgings provide uniformity of composition and structure. The thermal cycle and deformation process result in metallurgical recrystallization and grain refinement. In other words, it produces a steel product that is incredibly durable and impact-resistant.
Forged steel is stronger and more reliable than plate steel because its grain flows have been altered and conform to the shape of the part.
The advantages to using a forging include:
- The tight grain structure of a forging makes it mechanically reliable while offering superior wear resistance
- There are no porosity, cavities, or shrinkage
- It’s tougher than the alternatives
- It’s excellent at handling impact

How Do Forgings Differ from Castings?
While forging is applying thermal and mechanical energy to solid steel ingots or billets, castings are produced by pouring molten metal into a mold that has been made to the desired shape.
Parts that are too intricate or large for the forging process are often cast. The tooling (patterns and core boxes) that is used to produce castings is less expensive than forging dies. Depending on how the part will be used, however, the strength and reliability of forgings make it the better choice.

Ask us for a quote. You’ll find that accurately machined dies are not beyond your budget.
Request a free consultation and receive 20% off your first order.