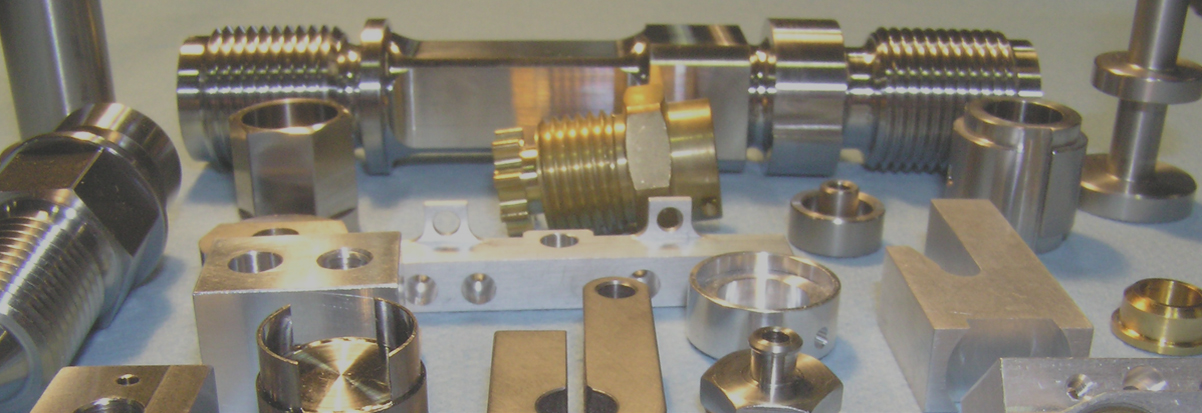
Brass Pipe Fittings
Product Details
Klikkon specialized in producing all kinds of brass fittings, brasss hose fittings, brass swivel fittings, brass tube fittings.
See more specifications below
Copper, brass, aluminum, and plastic tubing. Not recommended for steel tubing. Soft plastic tubing requires support inside and in line sleeve. Maximum working pressure is 400 psi. Nominal working pressure is 200 psi. -65˚ to +250˚F.
compression fitting components and assembly
how are they assembled?
1. Use a tube cutter on the tubing to cut to length and assure a clean straight cut.
2. Prepare the end of the tube with a deburring tool to assure a surface free of burrs.
3. Slide the nut and then the ferrule onto the tube. The thread end of the nut must face out.
4. Insert tubing into the fitting body, making sure the tube is bottomed out on the fitting shoulder.
5. Assemble the nut to the body, hand tight.
6. Tighten the nut to the body using a wrench to the number of turns indicated in the table to the right.
application parameters
types of tubing Designed for use with aluminum, copper and plastic tubing, not recommended for steel tube. Compression fittings are designed for medium pressure tubing where excessive vibration or tube movement is not involved. Not recommended for application using gaseous media. working pressures for aluminum or copper tubing Temperature and type of tubing are important factors. However, the following table is a good guide for proper selection at ambient temperatures of 73˚F
Note: For working pressures with plastic tubing, please see the tubing section of the klikkon catalog.
The pressure ratings will vary with the type tubing chosen. In any case use only with nylon or polyethylene tubing suitable for different pressure ranges
• low, medium compressed air pressure
• medium hydraulic pressure
• for compressed air, fuel oil, hydrocarbon, water…etc
extensive connection in all industrial fields
• many connection possibilities
• direct assembly, without soldering or tubing preparation
use to connect different types of tubing
• copper to brass
• plastic (nylon, polyurethane, fluoropolymer, PVC…)
• steel •
rubber
barbed fittings perfectly adapted to the requirements of industry:
• no tools are required and no nuts or collars to tighten
• connection to push-on hose
use to connect different diameter tubing
• with Reduction Assembly, different types and diameters of tubing can be easily connected.
technical specifications
To enable the user to obtain the best results fromKlikkonbrass compression fittings due regard to the application and tube used is necessary. As a guide the table below details the service pressures of the fitting assembly together with the service and burst pressures of various tubes. The pressures are expressed in psi and are provided in good faith – however they should be taken only as a guide and are not guaranteed.
brass tube: supplied in straight lengths: figures as above copper tube: supplied in coils: reduce the above service pressures by 35%. Do not use in areas of vibration.
These products include special connections, fluids compatibility, threads, shape, temperature, materials etc., which preclude the use of standard fittings.Klikkonis pleased to share its knowledge and experience to solve special problems.
STANDARD COMPRESSION FITTINGS are the most basic style of Compression Fitting made. This economical fitting is available in a wide range of off the shelf sizes and styles. ADVANTAGES These fittings are easy to assemble requiring no soldering, flaring or deburring. Standard Compression Fittings are suitable for a wide variety of applications. APPLICATIONS May be used with copper, aluminum, brass, plastic and steel tubing. Installation should be where low to medium pressures are encountered, and modest tube vibration/movement is involved. Suitable for hazardous liquids, oils and fuels. WORKING PRESSURES Generally, working pressure is dependent upon the type of tubing used and not the fitting, consequently the table shown should be used as a guide ONLY. ASSEMBLY
1. Slide the nut then sleeve onto the tube ensuring threaded end of nut is facing the sleeve.
2. If using a plastic tube, push a 261 Tube Insert into the tube to prevent the tube collapsing.
3. Insert the tube into the fitting until the tube has bottomed onto the fitting shoulder.
4. Screw the nut onto the fitting and tighten hand tight. Using the table below, follow the number of additional wrench turns.